(Created page with "''バーチャルキューイング''は、''コールバックオプション''とも呼ばれており、受信コールセンターで使われる一般の着信呼自動...") |
(Created page with "* '''顧客満足度の向上''':コールバックをリクエストした後、お客様は電話をかけたまま待機する必要はなく、別のことができま...") |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
''バーチャルキューイング''は、''コールバックオプション''とも呼ばれており、受信コールセンターで使われる一般の着信呼自動分配装置(ACD)の拡張機能です。 このオプションを使うと、待機時間が長い場合、サービスキュー内の順位を維持したままの電話切断、エージェントに接続する順番が近づいたらコールバックの実施ができます。 バーチャルキューイングのメリットは次のとおりです: | ''バーチャルキューイング''は、''コールバックオプション''とも呼ばれており、受信コールセンターで使われる一般の着信呼自動分配装置(ACD)の拡張機能です。 このオプションを使うと、待機時間が長い場合、サービスキュー内の順位を維持したままの電話切断、エージェントに接続する順番が近づいたらコールバックの実施ができます。 バーチャルキューイングのメリットは次のとおりです: | ||
| − | * ''' | + | * '''顧客満足度の向上''':コールバックをリクエストした後、お客様は電話をかけたまま待機する必要はなく、別のことができます。 |
| − | * ''' | + | * '''放棄率の減少''':お客様は、電話で待機する必要がないため、サービスリクエストを放棄する(つまり、コールバックを無視する)可能性が低くなります。 |
| − | * ''' | + | * '''通話時間の短縮''':バーチャルキューで待機している顧客は、最終的にエージェントに接続されたときに、長い待ち時間に対する苦情を訴える可能性が低くなります。 |
| − | * ''' | + | * '''通信コストの削減''': バーチャルキューで待機しているお客様は、音声チャネルを占有しません。 |
Revision as of 19:17, 27 May 2020
概要
Bright Patternコンタクトセンターのバーチャルキューのチュートリアルは Bright Patternのバーチャルキューのオプションの設定方法、レポート統計に対する影響について説明します。
バーチャルキューイングは、コールバックオプションとも呼ばれており、受信コールセンターで使われる一般の着信呼自動分配装置(ACD)の拡張機能です。 このオプションを使うと、待機時間が長い場合、サービスキュー内の順位を維持したままの電話切断、エージェントに接続する順番が近づいたらコールバックの実施ができます。 バーチャルキューイングのメリットは次のとおりです:
- 顧客満足度の向上:コールバックをリクエストした後、お客様は電話をかけたまま待機する必要はなく、別のことができます。
- 放棄率の減少:お客様は、電話で待機する必要がないため、サービスリクエストを放棄する(つまり、コールバックを無視する)可能性が低くなります。
- 通話時間の短縮:バーチャルキューで待機している顧客は、最終的にエージェントに接続されたときに、長い待ち時間に対する苦情を訴える可能性が低くなります。
- 通信コストの削減: バーチャルキューで待機しているお客様は、音声チャネルを占有しません。
How It Works
Bright Pattern Contact Center Virtual Queue works in the following way:
For each incoming service call, the system calculates its estimated waiting time (EWT) in the queue. If this time exceeds a threshold EWT value preconfigured for the given service, the system notifies the calling customer about the wait time and offers the customer the option of receiving a callback when it is the customer's turn to be connected to an agent. The customer can request the callback to be made to the phone from which the customer is calling, or to a different number that the customer can enter using the phone keypad. The original live call is then disconnected while the customer’s position in the service queue is maintained by the system as if the customer had remained on the line, hence the name Virtual Queuing.
When it is the customer’s turn to be connected to an agent, the system makes an outbound call (callback) to the designated callback number. Upon answer, this call is connected to an available agent.
Initiation of the callback may be done either on prediction that an agent will become available around the expiration of EWT calculated for the given call or via explicit agent reservation.
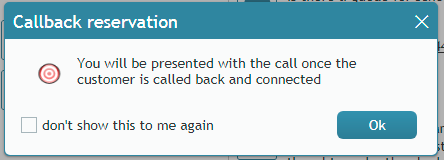
When agent reservation mechanism is used, the system will wait for an agent to become available before making a call. When the agent becomes available, she is reserved for the given call. The agent is then notified by a pop-up window that she has been reserved for a callback; this window includes the optional checkbox Dont's show this to me again should she not want to see the pop-up on future callback reservations.
While explicit agent reservation guarantees agent availability to take a callback, it is less efficient in terms of agent utilization as agents will have to spend some time in a reserved state; it can be recommended for services with small numbers of agents where EWT calculation is usually less precise.
When the EWT-based mechanism is used, the callback attempt is made a few seconds before EWT expiration based on the prediction that an agent will have become available by the time the callback is answered by the customer. If an agent does not become available at that time, the answered call is placed in the first position in the service queue to be connected to the next available agent. An interactive voice response (IVR) announcement can be played for the answered callback to prevent the customer from hanging up a call if it cannot be immediately connected to an agent.
Generally, for services with larger pools of agents, the EWT-based mechanism will reliably connect answered callbacks to agents without compromising their utilization.
Subsequent processing of answered callbacks delivered to agents is no different from the processing of calls waiting in the queue.