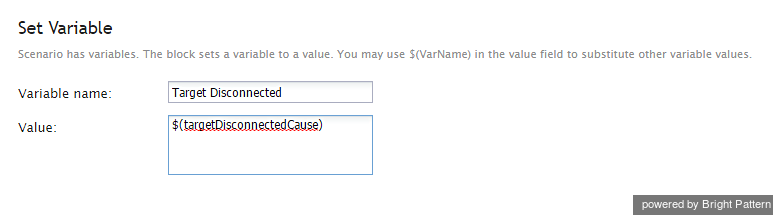
Set Variable
This block sets a value for a scenario variable.
Note it is possible to push variables directly to scenarios and workflows if the JavaScript API method postVariable is enabled.
Settings
Variable name
This is the name of the variable. The Variable name can be set to be anything you like.
Value
The Value is the desired variable value. In the example image shown, the value is $(targetDisconnectedCause), which is being used as a conditional exit in the scenario.
Variables in the $(varname) format can be used as values. Values can be specified as either expressions or literal strings. Literal strings are passed exactly as entered.
Expressions must begin with assignment sign = as the first character. For example, 2+2 will produce 2+2, whereas =2+2 will produce 4. The expression result produces one of the following data types: strings, integers, and floating point numbers.