Processing an inbound email interaction is initially determined by the email address that was used when sending the email. In the simplest case, email addresses correspond to email services (e.g., sales@company-name.com and support@company-name.com may be associated with Sales and Support services).
In a more complex configuration, analyzing keywords from email text helps to determine the appropriate services to associate with the email (e.g., an email coming to support@company-name.com can be categorized into Smartphone Support and Tablet Support services based on the presence of the words phone and tablet in the text of email messages.)
Unlike other types of scenario entries, email scenario entries do not refer to actual scenarios - "email scenario entries" is the name for the relationship between email addresses, their keywords, and any email services associated with the addresses and keywords. All information required for associating incoming emails with services is contained in the configuration settings for the email entries themselves.
Before configuring an email scenario entry, set up a corresponding email service and define all the known services so that emails arriving via this entry may be attributed and categorized properly. After the initial email entry is set up, more services and categorization rules can be added at any time.
Screen Properties
The screen properties for email scenario entries are organized into three tabs: Account, Services, and Case Fields. Each tab contains the following settings:
Account tab
Protocol type
Protocol type defines the protocols used to send and retrieve email messages. The following protocols are supported and provided in the drop-down menu: POP3/SMTP and Microsoft Graph.
Bright Pattern Contact Center software allows service providers to enable the Microsoft Graph API for OAuth email authentication on a cluster-wide basis.
Email settings are dependent on the selected protocol type.
POP3 Properties
Select the protocol type POP3/SMTP to expose and populate the following property fields for Incoming Mail and Outgoing Mail.
Account
- EMAIL ADDRESS
- The address that customers use to send emails to a specific service or a range of services. This address appears in the From: field of corresponding email replies as well as any outbound emails related to services associated with this scenario entry. This parameter is mandatory.
- DISPLAY NAME
- The name shown for the email address that customers use to send emails to a specific service or a range of services (e.g., "Bright Pattern Support" is a display name for "support@brightpattern.com"). This parameter is mandatory.
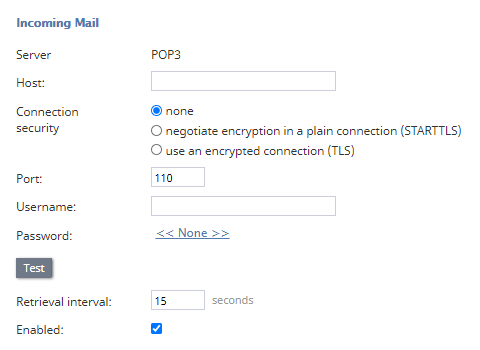
Incoming Mail
- SERVER
- The type of server used to transmit email messages to the email address. It is read-only. The POP3 protocol is supported.
- HOST
- The IP address or URL for the email server. This parameter is mandatory.
- CONNECTION SECURITY
- Select a cryptographic protocol (TLS or SSL) to secure this connection.
- For a nonsecure connection, select none.
- To negotiate encryption in a plain connection, select negotiate encryption in a plain connection (STARTTLS).
- For an immediate secure connection, select use an encrypted connection (TLS/SSL v3).
- PORT
- The port that is assigned to the server on the host. This parameter is mandatory.
- USERNAME
- The username for email client authentication. This parameter is mandatory.
- PASSWORD
- The password for email client authentication. This parameter is mandatory.
- TEST
- Used to test connection settings.
- ERROR REPORTED
- If the account is automatically disabled (see above), this parameter displays the error message that caused the system to disable the account. This parameter is read-only; the parameter's label is hidden while the testing attempt is successful.
- RETRIEVAL INTERVAL
- The retrieval interval is the mail retrieval period. By default, the account is checked for the presence of new mail every fifteen seconds. Some POP3 mail servers may be configured to lock out accounts that access mailboxes at this rate due to excessive activity. If this is the case, use this Incoming Mail, Retrieval interval parameter to increase the retrieval period to any value between 15 and 86400 seconds.
- ENABLED
- Enabled indicates whether the account is currently enabled. Accounts can be disabled manually or automatically, as described. Accounts can only be enabled manually.
- After incoming emails have been retrieved for processing, Bright Pattern Contact Center normally deletes those emails from the mailbox. However, if the POP3 server is configured for read-only access, the emails will stay in the mailbox and will be retrieved repeatedly until the system runs out of disk space. To prevent this from happening, the system will automatically disable the email account if an attempt to delete incoming mail returns an error from the POP3 server.
- If an account is disabled, you should check the Last error message. If the message indicates that the account has been disabled for the aforementioned reason, reconfigure your POP3 server for full access, and enable the account manually.
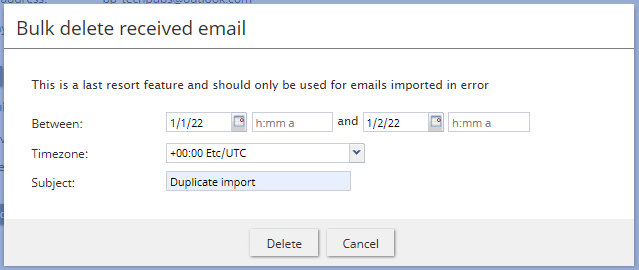
- BULK DELETE RECEIVED EMAIL
- This button allows you to delete emails received by the system in bulk. Specifically, when the button is selected a window pops, which allows you to configure emails to be deleted that were received between a range of dates and hours for a selected time zone.
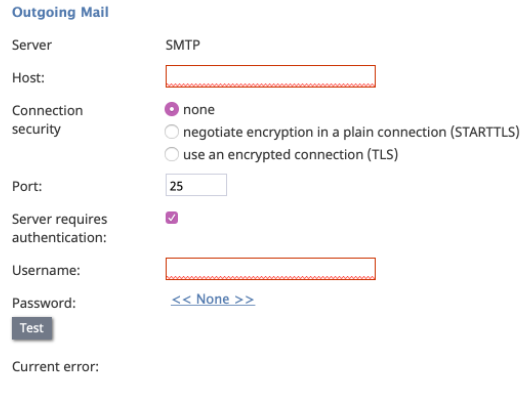
Outgoing Mail
- SERVER
- Server defines what protocol is used to send and retrieve email messages. It is read-only. The SMTP protocol is supported.
- HOST
- Host is the name of the host where the server is run. This parameter is mandatory.
- CONNECTION SECURITY
- Connection security provides indication of whether a cryptographic protocol (TLS or SSL) will be used to secure this connection.
- For a nonsecure connection, select none.
- To negotiate encryption in a plain connection, select negotiate encryption in a plain connection (STARTTLS).
- For an immediate secure connection, select use an encrypted connection (TLS/SSL v3).
- PORT
- Port is the port assigned to the server on the host. This parameter is mandatory.
- SERVER REQUIRES AUTHENTICATION
- Selecting the Server requires authentication checkbox forces the user to enter a username and password for email client authentication. If you do not select the checkbox, a username and password will not be necessary.
- USERNAME
- Username is the username for email client authentication. This parameter is mandatory.
- PASSWORD
- Password is the password for email client authentication. This parameter is mandatory.
- TEST
- The Test button is used to verify the correctness of your connection settings.
- ERROR REPORTED
- In case the account has been disabled automatically (see above), this parameter displays the error message that caused the system to disable the account. This parameter is read-only; the parameter's label is hidden while the testing attempt is successful.
- CURRENT ERROR
- The label Current error is displayed if the account type is enabled by your service provider and the last retrieval or send attempt was not successful; the label is hidden if both the last retrieval and last send did not have an error. If the account type is not enabled by your service provider , the label Current error is not shown. The content of this field is reset when the account is changed from disabled to enabled
Microsoft Graph
Selecting protocol type Microsoft Graph will bring up the following properties for Incoming Mail and Outgoing Mail. Note that this option must be enabled by the service provider.
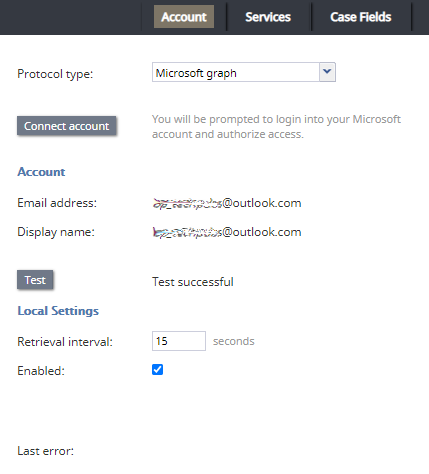
- Connect account
- When selecting the Connect account button, a separate window will pop and you will be prompted to log into your Microsoft account and authorize access. The application can request grant permissions, so you will need to give the required permissions to the application.
| If you are already signed into a Microsoft email account, a session cookie will be detected and credentials will not need to be entered | ||
- When an account is successfully connected, the email address will appear in the Email address field and the Display name field below. For more information, see the section How to Configure Microsoft Email Account Access Using Microsoft Graph
Account
- EMAIL ADDRESS
- When your Microsoft account has been successfully authorized and connected to your contact center, the email address will appear in this field.
- DISPLAY NAME
- When your Microsoft account has been successfully authorized and connected to your contact center, the email’s display name will appear in this field.
- Test
- The Test button is used to verify the correctness of your connection settings.
- ERROR REPORTED
- In case the account has been disabled automatically (see above), this parameter displays the error message that caused the system to disable the account. This parameter is read-only; the parameter's label is hidden if the testing attempt is successful.
Incoming Mail
- RETRIEVAL INTERVAL
- This setting allows you to define the mail retrieval period. By default, the account is checked for the presence of new mail every 15 seconds.
- ENABLED
- Enabled indicates whether the account is currently enabled. Accounts can be disabled manually or automatically, as described. Accounts can only be enabled manually.
- CURRENT ERROR
- The label Current error is displayed if the account type is enabled by your service provider and the last retrieval or send attempt was not successful; the label is hidden if both the last retrieval and last send did not have an error. If the account type is not enabled by your service provider, the label Current error is not shown. The content of this field is reset when the account is changed from disabled to enabled.
- BULK DELETE RECEIVED EMAIL
- This button allows you to delete emails received by the system in bulk. Specifically, when the button is selected a window pops, which allows you to configure emails to be deleted that were received between a range of dates and hours for a selected time zone. Note that you must select the Delete button in the window in order to confirm the bulk deletion.
Services tab
The Services tab presents settings related to email services.
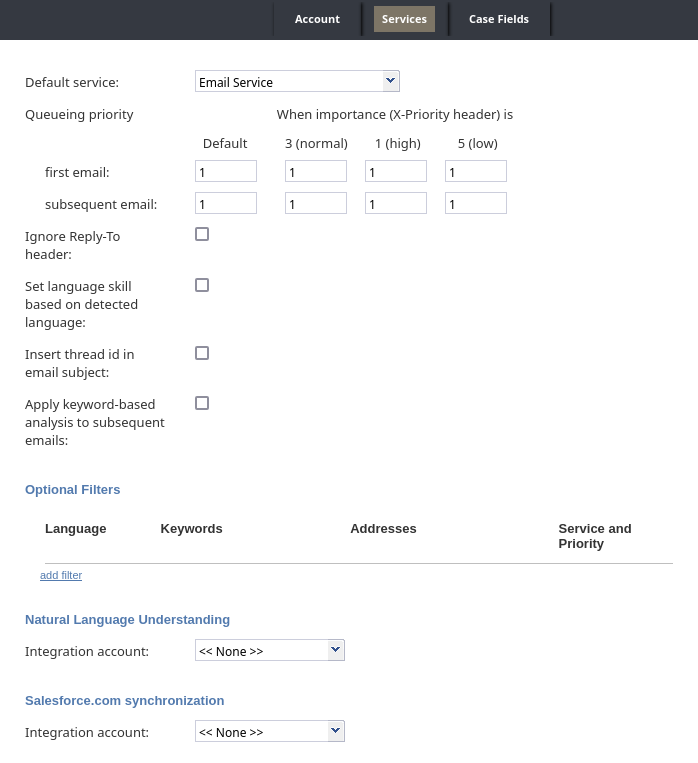
- Default service
- Default service is the email service that will be associated with emails arriving via this entry if categorization rules are not set or do not provide any keyword matches. This parameter is mandatory.
|
If you intend to delete an email service you must reassign this setting to another email service to move all existing emails to that new service. | ||
It is recommended to not allow the deletion of the last remaining email service if there are any emails in the service’s push queue or pull queue; however, it is OK to delete the last email service if there are emails in a case’s activity history or in an agent’s list of pinned cases.
- Queueing priority
- Queueing priority is the priority that will be given to emails received by this email scenario entry. Priority determines the position of the email interaction requesting the default service in the queue (i.e., Team Queue and Personal Queue), relative to email interactions associated with other services that are competing for the same agents.
Priority is set by the email sender in the form of an X-Priority header.
For more information regarding configuring queueing priority, see Tutorials for Admins, section Configuring High-Importance Email Routing.
- When importance (X-Priority header) is
- There are four options (i.e., columns) for importance. They are:
- Default
- This column allows you to define the queue placement for emails without X-Priority headers
- 3 (normal)
- This column allows you to define the queue placement for emails received with an X-Priority header value of 3.
- 1 (high)
- This column allows you to define the queue placement for emails received with an X-Priority header value of 5.
- 5 (low)
- This column allows you to define the queue placement for emails received with an X-Priority header value of 1.
| ||
- First email
- This row allows you to define the queueing priority for all new incoming emails (i.e., not replies); you may set priority for all four When importance (X-Priority header) is column options.
- Subsequent email
- Subsequent email priority is the queuing priority of customer emails related to existing email threads.
- The system automatically checks whether an incoming email may be part of an existing email thread (e.g., after receiving a reply to an original email request, the customer may have additional questions). Such emails bypass the keyword-based analysis. Instead, they are automatically attributed to the same service as the original request. This parameter allows you to distribute such emails with a higher (or lower) priority than any new email requests.
- Ignore Reply-To Header
- The Ignore Reply-To Header checkbox, when selected, allows the system to ignore the header in the reply-to field of an email. When this setting is checked, the behavior is as follows:
- The From field is used for identification.
- The From field is used for agent replies.
- The Return-Path header is used for auto-replies.
- If this setting is unchecked, the behavior is as follows:
- If a reply-to header is present, it is used for identification, agent replies, and auto-replies.
- If a reply-to header is missing, the behavior is the same as if the Ignore Reply-To Header box is checked.
- Set Language Skill Based on Detected Language
- The Set Language Skill Based on Detected Language checkbox, when selected, allows the following:
- Emails with undetected languages will be sent to the default email service regardless of keyword matches.
- If the detected language of an email is not in the call center's list of configured languages, the email will be sent to the default email service, regardless of keyword matches.
- Insert thread id in email subject
- When disabled, the Insert thread id in email subject checkbox excludes the email case’s thread ID from the email’s subject line. Note that this setting is automatically enabled for existing email entries; if you are creating a new scenario entry for email, this setting is not enabled.
- Apply keyword-based analysis to subsequent emails
- When enabled, each subsequent email associated with a case is subjected to keyword analysis. As a result, the associated case can be routed to a different service according to the following conditions:
- If no matching keywords are detected in the subsequent email, the case will remain associated with its current service.
- If an agent is busy with the case when a subsequent email is being routed, the case will remain associated with its current service, even if matching keywords were found in the new email.
- Otherwise, if routing occurs while the case is in a queue:
- The case will be associated with the service indicated by the keyword-based analysis .
- The activity history of the case will show "Transferred by routing to [service name] on [date] at [time]".
- This transfer will be reflected in transfer-related metrics in all reports.
- The target answer time is recalculated according to the configuration of the newly associated service.
- When this option is disabled, subsequent emails of an existing case are automatically routed to the service first associated with the case.
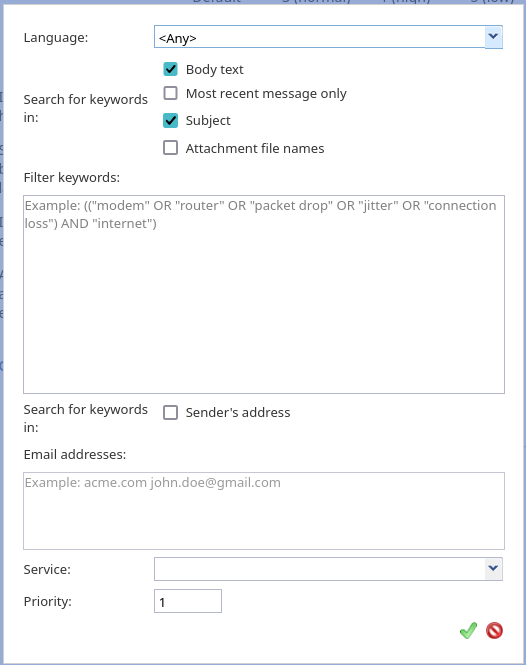
- Optional Filters
- Optional Filters allow you to assign emails incoming to the scenario to different services based on keyword analysis of the email subject, body text, or attachment file names.
- To add a filter, click "add filter".
- Filters are checked for possible keyword matches in the order in which they appear on the list. As soon as a match is found, the corresponding service and priority are assigned to the email interaction. Note that this order may be affected by the language setting of the filter. See the description of the Language setting for more details.
- Newly created filters will appear at the end of the list. To change the position of a filter in the list, drag it to the desired location.
- To edit or remove an existing filter, hover over it and select the desired function.
- Each filter is defined by the following options:
- Language
- The Language setting is where you select the language in which the keywords of the given filter will be written. This setting only matters if the filter’s keywords may have different meanings in different languages. Otherwise, leave this parameter set to the default value <Any>. The list of languages here is limited to the configured Language Skills that are auto-detectable.
- Initially, the system will try to detect the language of the email text automatically. If the language is not identified, only the filters set to Any will be checked for keyword matches. If the language is identified, the system will first check the filters set to Any and then check the filters set to the detected language.
- Search for keywords in
- Specify which parts of an email to check for matching filter keywords. The following options are available:
- Body text
- Searches the email body text for matching keywords.
- Most recent message only
- When selected, keyword analysis will be applied only to the most recent message in the body text of an email. The parts of the body text which appear to be previous messages in the email thread will be ignored. Typically, this option is selected in conjunction with the Apply keyword-based analysis to subsequent emails option to give greater precedence to keywords in the most recent communication.
- When this option is not selected, keyword filtering is applied to the entire body text of the email, including text which appears to be previous messages in the email thread.
- Subject
- Searches the email subject line for matching keywords.
-
- Attachment filenames
- Searches the filename of each attachment for matching keywords. Keyword analysis does not require an exact match to the filename. A keyword can be identified within a filename string regardless of whether it appears before, in between, or after spaces, dashes, underscores, or periods.
- Filter keywords
- Filter keywords are the keyword expressions that you specify. Each keyword/phrase in the expression must be set in quotation marks. Logical expressions can include logical operators AND, OR, XOR, NOT, and parentheses (e.g., “connection loss” AND (“router” OR “modem”)).
- Search for keywords in sender's address
- The Search for keywords in sender's address checkbox lets you include or exclude an incoming email's From field in a keyword search. When this option is selected, you must define your keywords in the Email addresses field. Note that this option is unchecked by default.
- Email addresses
- The Email addresses field allows you to define email addresses that will be used to filter an incoming email by the contents of the From field. You may enter complete addresses (e.g. jane.doe@brightpattern.com), domains (e.g., brightpattern.com), or both. A domain can be specified both with and without the “@” character. If you use several addresses and/or domains, they can be separated by space, comma, or semicolon. Quotation marks should not be used when specifying anything in this field.
- Service and Priority
- The Service is the email service that will be associated with email interactions matching this filter.
- The Priority is the priority that will be assigned to email interactions matching the filter. For more information about email priority, see the description of the Default priority setting.
Natural Language Understanding
Our contact center solution integrates with IBM Watson to provide Natural Language Understanding (NLU) functionality and sentiment analysis capabilities to your tenant on a per-service basis. To enable NLU for email scenario entries, select the applicable integration account from the Natural Language Understanding drop-down menu.
- Integration account
- The default integration account is < < None > >. If no integration accounts are listed, that means no integration accounts of the type "Natural Language Understanding" have been configured for your tenant. To add an integration account, see section Integration Accounts of the Contact Center Administrator Guide.
Salesforce.com synchronization
If your contact center is integrated with Salesforce.com (SFDC), emails from the Agent Desktop application can be synchronized with SFDC for routing and reporting. Emails from Agent Desktop link to SFDC Person Accounts, Contacts, and Accounts.
| You may configure Screenpop URL to make synchronized SFDC cases pop in Agent Desktop. | ||
With this setting enabled, the following happens for all incoming and outgoing email:
- Emails are received and processed by agents in Agent Desktop.
- After emails are processed, the system conducts a search in Salesforce.com using Salesforce Object Query Language (SOQL). The search looks in Contact objects for field Email (i.e., the customer's email, specifically “from” or “to” fields based on the message direction). The search also looks in Users objects for field Email (i.e., the agent’s email, specifically the “from” field based on message direction).
- If multiple matches are found, the search takes the first result.
- If a new Agent Desktop case was created, a new SFDC case is created.
- Whether a match was found or a new case was created, the system creates an EmailMessage object for the match, which passes case ID, related case ID, activity ID, and attachment data.
- If an email contains an attachment, the system creates an Attachment object.
- Finally, the system creates a Task object, which contains user, case, account, and contact data.
If neither a matching contact nor a matching user is found, the case is not created (i.e., only known addresses are synchronized); if the case is not created, neither the first nor subsequent messages are synchronized.
If the Screenpop URL setting is configured with a Salesforce URL, note the following:
- After emails are received and processed in Agent Desktop, cases and emails are synchronized to SFDC as cases and emails in Activity history, and they are linked to an agent (user) and a contact.
- The first email routed in such a way results in a screen pop of the customer/contact record in SFDC.
- Agent Desktop will also display the contact and activity history (if contact feature is used).
- Each subsequent email results in a screen pop of the SFDC case.
- Bright Pattern Contact Center would retain all of the routing control and reporting data. Switching between two screens (Agent Desktop and SFDC) is required.
| Bright Pattern and SFDC need to be integrated on both the server and client side. For more information on SFDC integration, see the Salesforce.com Integration Guide. | ||
- Integration account
- The default integration account is < < None > >. If no integration accounts are listed, that means no integration accounts of the type "Salesforce.com" have been configured for your tenant. To add an integration account, see the Integration Accounts of the Contact Center Administrator Guide.
Case Fields Tab
You may utilize custom case fields when configuring email to pull data from email subject line and body; these custom case fields then can be used in custom reporting fields.
- Parse email Subject into case fields
- To create case fields from the text in an email subject line, you will need to first configure a regex expression. Once this has been configured, name the configured expression in the case field field.
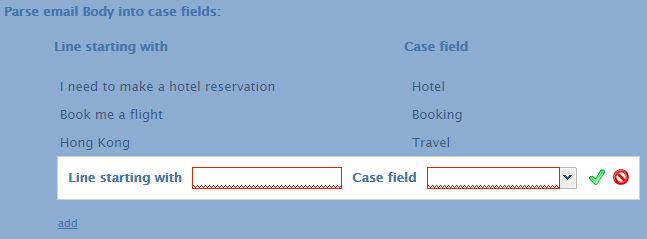
- Parse email Body into case fields
- To create case fields from the text in an email body, enter in words or phrases your customers use at the beginning of sentences in the Line starting with field. Once configured, name the field in case field.