Matt.lashley (talk | contribs) m |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | <translate> | + | <translate> |
| − | |||
| − | + | = Fetch URL= | |
| + | The '''Fetch URL''' scenario block retrieves web content, including JSON-formatted data, from a URL, using a specified method and parses it into scenario variables. | ||
| − | + | {{Note | HTTP, HTTPS and basic authentication are supported.}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
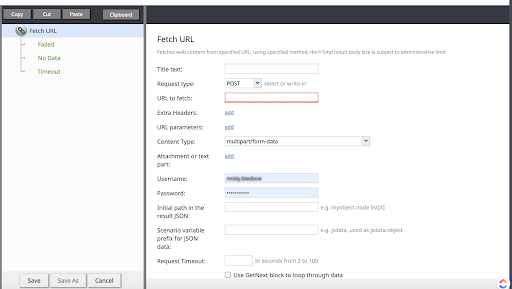
| + | {{Image850 | Fetch-url-scenario-block-01-2023-03-23.png | The Fetch URL scenario block.}} | ||
| − | == | + | === Conditional Exits === |
| − | + | The Fetch URL block may take one of three conditional exits: | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ;Failed | |
| − | + | :The Failed conditional exit is taken if an error occurred during the HTTP method execution. See HTTP Response Codes below for details. | |
| + | ;No Data | ||
| + | :The No Data conditional exit is executed if no data is returned in the body of the HTTP response. | ||
| + | ;Timeout | ||
| + | :The Timeout conditional exit executes when the processing time exceeds the value entered in the '''Request Timeout''' field. | ||
| − | + | === Settings === | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ; Title text | |
| − | + | : The name of the instance of the block displayed in the flowchart. | |
| − | + | ; Request type | |
| − | + | :The HTTP method used in the fetch. | |
| − | + | :{| class="wikitable" | |
| − | + | |- | |
| + | ! Request Type (HTTP Method) | ||
| + | ! Content Type | ||
| + | ! Notes | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | GET | ||
| + | | Application/json | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | POST | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | * Application/json | ||
| + | * Multipart/form-data | ||
| + | * Single file upload, content-type set below | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | * Allows adding multiple attachment or text parts | ||
| + | * Content type is optional. If not specified, the system uses the attachment’s content type | ||
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | PUT | |
| + | | Application/json | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PATCH | ||
| + | | Application/json | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | DELETE | ||
| + | | Application/json | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | ; URL to fetch | |
| − | '' | + | : The HTTP/HTTPS URL of the web resource that this block will access. Query string parameters, if any, should be specified in the URL parameters (see below). If parameters are defined, they will be appended to the URL, and the '?' and '&' separators will be automatically inserted. |
| − | + | ; Extra headers | |
| + | : The HTTP headers to add to the request (e.g. for authentication purposes). Functions can be used by inserting them as a value. Click '''add''' to define a header, type in the ''name'', and type in the ''value''. | ||
| − | + | {{LightBulb | For example, a payment gateway may have a RESTful interface that requires authentication via “Authorization” header and SHA-256 hash of time, username, and password. To enable authentication, you would provide a request header with the ''name'' “Authorization” and the ''value'' ''“accessid hmac(“SHA-256”, key, message)”''.}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | : For more information about Scenario Builder functions, see [[scenario-builder-reference-guide/Built-inFunctions | Built-in Functions]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ; URL parameters | |
| − | '' | + | : The parameters to be URL encoded and appended to the URL. Scenario variables can be used by inserting them as ''$(varname)''. Click '''add''' to define URL parameters, type in the name, and type in the value. |
| − | + | ; Content Type | |
| − | + | : The type of data to be submitted in request body. | |
| − | + | : Select ''application/json'' for a JSON data structure, or select ''application/x-www-form-urlencoded'' for a URI-encoded data in the body of the message. | |
| − | |||
| − | = | + | :{| class="wikitable" |
| − | + | |- | |
| + | ! Content Type | ||
| + | ! Request Type (HTTP Method) | ||
| + | ! Notes | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Application/json | ||
| + | | GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Multipart/form-data | ||
| + | | POST | ||
| + | | Allows adding multiple attachment or text parts | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Single file upload, content-type set below | ||
| + | | POST | ||
| + | | Content type is optional. If not specified, the system uses the attachment’s content type. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | ; Body | |
| − | This | + | : This property is displayed when the ''Content Type'' is set to ''application/json'' and specifies the data to be transmitted with the given request in JSON format. Scenario variable substitutions are allowed. |
| − | ''' | + | ; Form parameters |
| + | : This property is displayed when the ''Content Type'' is set to ''application/x-www-form-urlencoded'' and is used to specify the data to be transmitted with the given request as a URL-encoded key/value string. To define each parameter, click '''add''', type in the parameter name, and set the value. Scenario variable substitutions are allowed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ; Username | ||
| + | : The request authentication username. Variable substitutions are allowed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ; Password | ||
| + | : The request authentication password. Variable substitutions are allowed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ; Initial path in the result JSON | ||
| + | : If the response body contains JSON, this setting can be used to save into scenario variables a specific part of the data. Example: ''myobject.node.list[4]''. The default is "none"; the path starts from the root of the returned JSON. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ; Scenario variable prefix for JSON data | ||
| + | : This string will be used as the name of the variable to receive parsed JSON data. Note that if the initial path above points to an array, depending on the value of the ''GetNext'' option, this variable would either contain the array or its first (and subsequent) elements. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ; Request timeout | ||
| + | : This option allows sets a timeout for situations when processing external web service APIs run longer than expected, enabling the system to move to the next block if there is no API response within the time configured. The range for this field is between 2 and 100 seconds; when left blank, the set time defaults to 100 seconds. Note that this field is present only if an explicit value is entered. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ; Use GetNext block to loop through data | ||
| + | : This box is selected if the JSON response data (at the initial path) is an array. The scenario variable will be set to the first element of the array and GetNext block could be used to iterate over the array elements, setting scenario variable to the next element. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Note | If '''GetNext''' is enabled, the behavior of the Fetch URL block will be the same as it was for Bright Pattern Contact Center version 3.13 and earlier.}} | ||
| Line 72: | Line 128: | ||
| − | == Response Data Handling == | + | === Response Data Handling === |
| + | |||
In all cases, the response data is limited to 50 KB. | In all cases, the response data is limited to 50 KB. | ||
| Line 87: | Line 144: | ||
Possible syntax for the initial path setting and the access to the data saved in the scenario variable is as follows: | Possible syntax for the initial path setting and the access to the data saved in the scenario variable is as follows: | ||
| − | * ''item. | + | * ''item. Subitem'' |
* ''item[index]'' | * ''item[index]'' | ||
* ''item[attr1=value].attr2'' | * ''item[attr1=value].attr2'' | ||
| Line 93: | Line 150: | ||
| − | == Fetch URL Result Code Based On HTTP Response Codes == | + | === Fetch URL Result Code Based On HTTP Response Codes === |
| + | |||
The status code and the body of the received HTTP response will be stored in local variables ''$(integrationResultCode)'' and ''$(integrationResultBody)'', respectively. For troubleshooting purposes, you may use the [[scenario-builder-reference-guide/EMail|EMail]] or [[scenario-builder-reference-guide/InternalMessage|Internal Message]] block to obtain content of responses indicating a failed attempt. For more information, see the description of variable [[scenario-builder-reference-guide/Variables|''$(integrationResultBody)'']]. | The status code and the body of the received HTTP response will be stored in local variables ''$(integrationResultCode)'' and ''$(integrationResultBody)'', respectively. For troubleshooting purposes, you may use the [[scenario-builder-reference-guide/EMail|EMail]] or [[scenario-builder-reference-guide/InternalMessage|Internal Message]] block to obtain content of responses indicating a failed attempt. For more information, see the description of variable [[scenario-builder-reference-guide/Variables|''$(integrationResultBody)'']]. | ||
| Line 109: | Line 167: | ||
=== HTTP Redirect Response Handling === | === HTTP Redirect Response Handling === | ||
| + | |||
The Fetch URL block handles 3xx Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) response codes in the following way. | The Fetch URL block handles 3xx Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) response codes in the following way. | ||
| Line 125: | Line 184: | ||
* 305 Use Proxy (since HTTP/1.1) | * 305 Use Proxy (since HTTP/1.1) | ||
* 306 Switch Proxy | * 306 Switch Proxy | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</translate> | </translate> | ||
Revision as of 12:42, 21 September 2023
<translate>
Fetch URL
The Fetch URL scenario block retrieves web content, including JSON-formatted data, from a URL, using a specified method and parses it into scenario variables.
| HTTP, HTTPS and basic authentication are supported. | ||
Conditional Exits
The Fetch URL block may take one of three conditional exits:
- Failed
- The Failed conditional exit is taken if an error occurred during the HTTP method execution. See HTTP Response Codes below for details.
- No Data
- The No Data conditional exit is executed if no data is returned in the body of the HTTP response.
- Timeout
- The Timeout conditional exit executes when the processing time exceeds the value entered in the Request Timeout field.
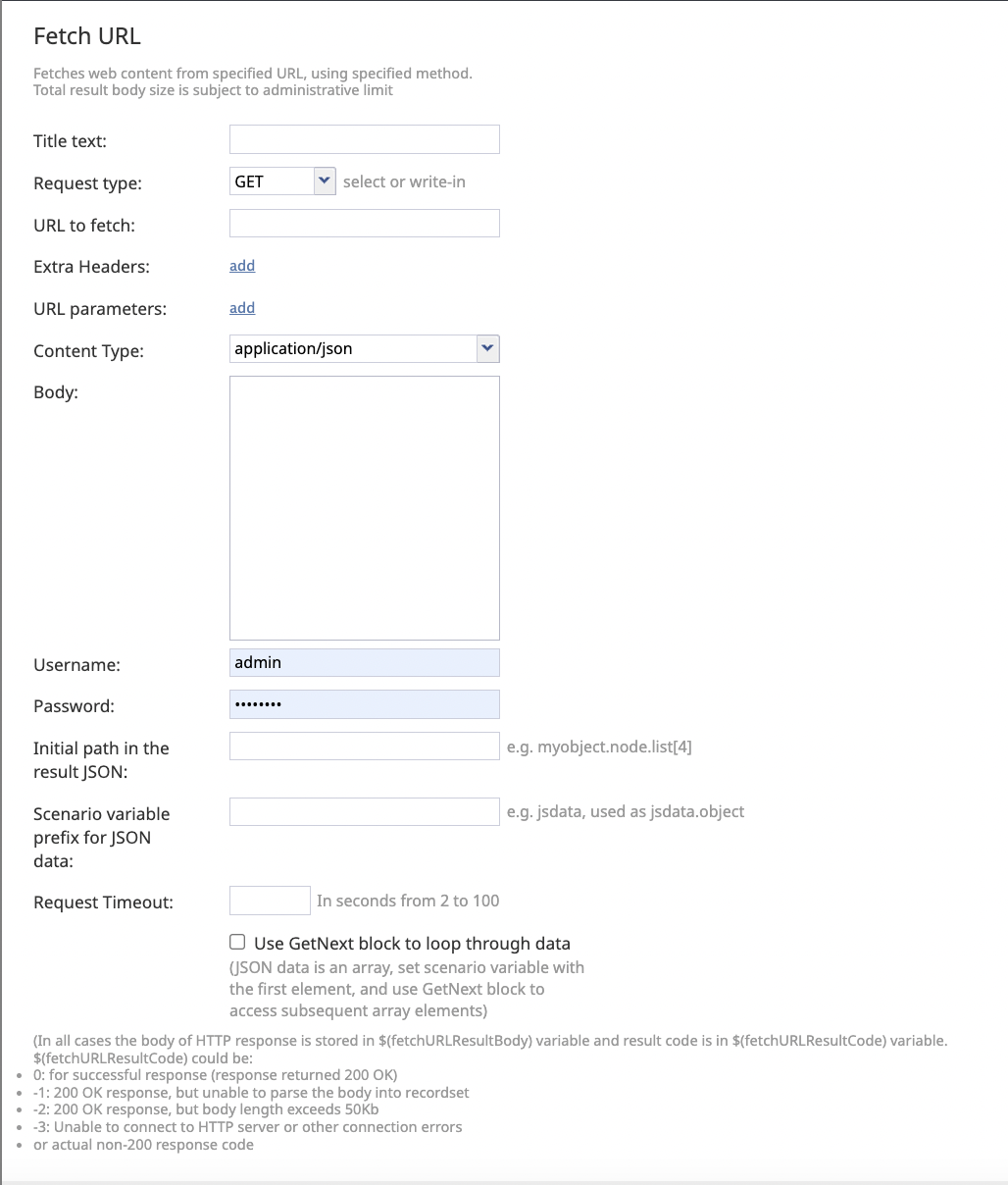
Settings
- Title text
- The name of the instance of the block displayed in the flowchart.
- Request type
- The HTTP method used in the fetch.
Request Type (HTTP Method) Content Type Notes GET Application/json POST - Application/json
- Multipart/form-data
- Single file upload, content-type set below
- Allows adding multiple attachment or text parts
- Content type is optional. If not specified, the system uses the attachment’s content type
PUT Application/json PATCH Application/json DELETE Application/json
- URL to fetch
- The HTTP/HTTPS URL of the web resource that this block will access. Query string parameters, if any, should be specified in the URL parameters (see below). If parameters are defined, they will be appended to the URL, and the '?' and '&' separators will be automatically inserted.
- Extra headers
- The HTTP headers to add to the request (e.g. for authentication purposes). Functions can be used by inserting them as a value. Click add to define a header, type in the name, and type in the value.
- For more information about Scenario Builder functions, see Built-in Functions.
- URL parameters
- The parameters to be URL encoded and appended to the URL. Scenario variables can be used by inserting them as $(varname). Click add to define URL parameters, type in the name, and type in the value.
- Content Type
- The type of data to be submitted in request body.
- Select application/json for a JSON data structure, or select application/x-www-form-urlencoded for a URI-encoded data in the body of the message.
Content Type Request Type (HTTP Method) Notes Application/json GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE Multipart/form-data POST Allows adding multiple attachment or text parts Single file upload, content-type set below POST Content type is optional. If not specified, the system uses the attachment’s content type.
- Body
- This property is displayed when the Content Type is set to application/json and specifies the data to be transmitted with the given request in JSON format. Scenario variable substitutions are allowed.
- Form parameters
- This property is displayed when the Content Type is set to application/x-www-form-urlencoded and is used to specify the data to be transmitted with the given request as a URL-encoded key/value string. To define each parameter, click add, type in the parameter name, and set the value. Scenario variable substitutions are allowed.
- Username
- The request authentication username. Variable substitutions are allowed.
- Password
- The request authentication password. Variable substitutions are allowed.
- Initial path in the result JSON
- If the response body contains JSON, this setting can be used to save into scenario variables a specific part of the data. Example: myobject.node.list[4]. The default is "none"; the path starts from the root of the returned JSON.
- Scenario variable prefix for JSON data
- This string will be used as the name of the variable to receive parsed JSON data. Note that if the initial path above points to an array, depending on the value of the GetNext option, this variable would either contain the array or its first (and subsequent) elements.
- Request timeout
- This option allows sets a timeout for situations when processing external web service APIs run longer than expected, enabling the system to move to the next block if there is no API response within the time configured. The range for this field is between 2 and 100 seconds; when left blank, the set time defaults to 100 seconds. Note that this field is present only if an explicit value is entered.
- Use GetNext block to loop through data
- This box is selected if the JSON response data (at the initial path) is an array. The scenario variable will be set to the first element of the array and GetNext block could be used to iterate over the array elements, setting scenario variable to the next element.
| If GetNext is enabled, the behavior of the Fetch URL block will be the same as it was for Bright Pattern Contact Center version 3.13 and earlier. | ||
Response Data Handling
In all cases, the response data is limited to 50 KB.
If the response data is not JSON-encoded, it could be accessed as string via the $(integrationResultBody) scenario variable described below.
If the response data is JSON, the following will happen:
- It will be parsed.
- If the "GetNext" option is enabled and the item the initial path is pointing to is a regular, non-associative array:
- The scenario variable will be set to the first item of the array.
- The GetNext block could be used to initialize the variable to the next and subsequent items.
- Otherwise, the scenario variable will be set to the item to which the initial path is pointing.
Possible syntax for the initial path setting and the access to the data saved in the scenario variable is as follows:
- item. Subitem
- item[index]
- item[attr1=value].attr2
- combinations (e.g., item.subitem.array[index].value.array[attr=x].value)
Fetch URL Result Code Based On HTTP Response Codes
The status code and the body of the received HTTP response will be stored in local variables $(integrationResultCode) and $(integrationResultBody), respectively. For troubleshooting purposes, you may use the EMail or Internal Message block to obtain content of responses indicating a failed attempt. For more information, see the description of variable $(integrationResultBody).
For backward compatibility reasons, the code and the body of the received HTTP response are also stored in local variables $(fetchURLResultCode) and $(fetchURLResultBody).
The possible values of the $(fetchURLResultCode) variable are as follows:
- 0: 200 OK response (i.e., a successful HTTP request response)
- -1: 200 OK response, but unable to parse the body into recordset
- -2: 200 OK response, but body length exceeds 50 KB
- -3: Unable to connect to HTTP server or other connection errors
- -4: Incorrect JSON syntax in the request body when using PUT or POST requests
- Other: Actual non-200 HTTP response code, such as 400 or 500
Note: When responding with error codes like 500, some servers will not provide any extra information. If there is extra info, it is passed as a plain string to the scenario. From this point, you may check the specific web server for reported errors (if any) or use regex to extract details from the response body.
HTTP Redirect Response Handling
The Fetch URL block handles 3xx Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) response codes in the following way.
When the following codes are received, the block retries the request to the provided redirect URL using the GET request method:
- 301 Moved Permanently
- 302 Found
- 303 See Other (since HTTP/1.1)
When the following codes are received, the block retries the request to the provided redirect URL using the originally specified request method:
- 307 Temporary Redirect (since HTTP/1.1)
- 308 Permanent Redirect (RFC 7538)
When the following status codes are received, the conditional exit Failed will be selected:
- 300 Multiple Choices
- 304 Not Modified (RFC 7232)
- 305 Use Proxy (since HTTP/1.1)
- 306 Switch Proxy
</translate>